Bachelor of
Journalism
(BOJ)
What is Journalism?
Journalism is a science that teaches how to produce content based on real events to be disseminated to various platforms. Students of Journalism Study Program will learn all forms of journalism (whether it is writing, audio, visual or audio visual) ranging from the process of planning, production, dissemination / publication, to monitoring the content on social media.
In today’s industrial era, a journalist does not only make news. UMN’s Journalism Study Program also provides opportunities for students to become content creators who can focus on producing content in accordance with topics of interest, for example, travelling to a certain place, sports matches, the current state of the environment, or any other topic that is out there. Students will learn how to build the content according to the audience they want to target.


Why Choose
UMN’s Journalism?
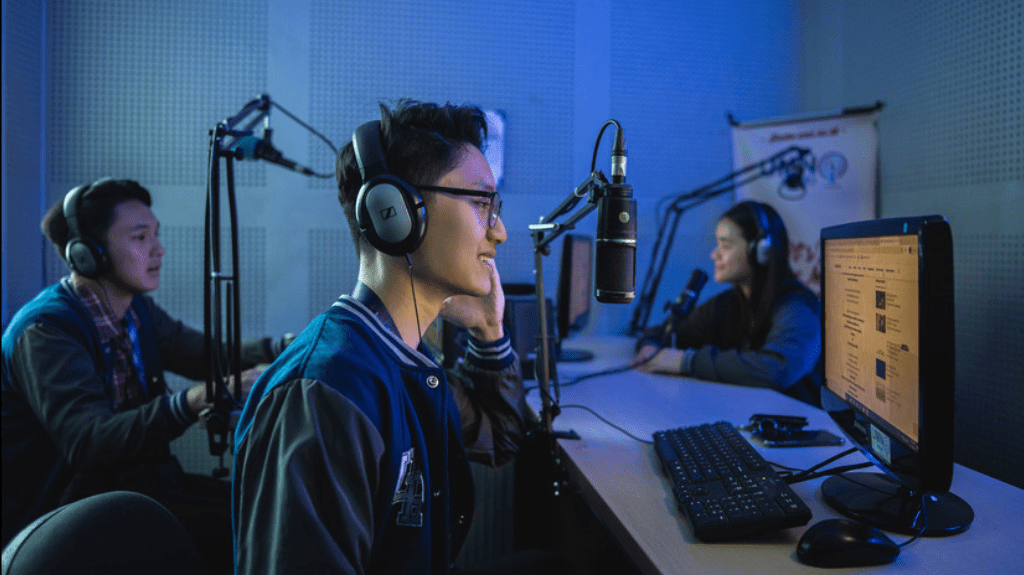
Multimedia Nusantara University’s Journalism Study Program focuses on utilizing new technologies to learn new forms of journalism. Therefore, learning activities are also supported with adequate technology. Some courses are also tailored to the needs of the industry as well as the development of existing technologies, such as mobile and social media journalism courses that utilize the use of gadgets in producing and disseminating journalistic products through social media.
In addition, UMN’s Journalism Study Program also equips its students with the knowledge about hoax news (HOAKS) and ways to identify them through digital factchecking courses. Besides that, through web apps for journalism courses, students will also be taught how to create a website to be able to publish journalistic products that have been created independently.
Kompas Gramedia supports UMN in providing access to teachers from media industry who are experienced, able to provide knowledge about the current conditions of the media industry and serve a source for students to practice directly.
National Accreditation

General Information
| Credits | 241.92 (ECTS) / 144 (SKS) |
| Education Type | Bachelor Program |
| Duration | 4 years |
| Language | Indonesia & English |
| Bachelor's Degree | Bachelor of Communication Science (S.I.Kom.) |
| Type of Program | Full-time |
Vision & Mission
Vision
To become a Multimedia Journalism Undergraduate Study Program that is excellent in exploring new forms of journalism and producing graduates who are internationally minded, able to master the theory and practice in the field of journalism based on Information and Communication Technology (ICT), and possess entrepreneurial spirit, as well as noble character.
Mission
- Organizing an experiential learning process that has high quality and virtue, supported by professional teachers and curriculum that is in line with the development of journalism and ICT.
- Carrying out research programs in the field of multimedia journalism that contribute to the development of journalism.
- Carrying out community service activities related to the field of multimedia and journalism.
Career Prospect
Graduates of Journalism Study Program can work in the field of communication, journalism, or creative industries. Some of the graduates’ profiles can be seen below :
Reporter, announcer, News Anchor, Host Program, News Editor, Executive Produer, Camera Persons, Photojournalist, Script Writer, Content Writer, Columnist, Creative Writer, Creative Production, Publisher, Media Researcher and Analyst.
Further Study
Graduates of UMN’s Journalism Study Program can continue their studies in the field of communication, public relations, and other social sciences.
Partnership & Collaborations
UMN’s Journalism Study Program has been working with several media in Indonesia such as Kompas Gramedia Group, Tempo, SCTV, CNN TV, and other national media outlets to obtain resources and provide real experience for students in the media industry.
We have also networked with the Press Council and some communities such as the Alliance of Independent Journalists (AJI) and Jurnokoders in the creation of several programs related to journalistic learning.
In the international sphere, UMN’s Journalism Study Program collaborates with Google, especially in the Google News Initiative and the International Federation of Journalists (IFJ) in organizing different activities. UMN’s Journalism Study Program also collaborates with UNESCO that contributes to the curriculum used. In addition, we also cooperate in several other activities, one of which is our involvement in the implementation of world press Freedom Day.
Student Scholarship
UMN scholarship program is offered to high school students in 12th grade who have academic, sports, and artistic achievements while in 11th grade. In addition, UMN also offers the program to high school/vocational school students who won medals in the National and International Science Olympics. As a form of appreciation for the dedication of teachers and employees/ staff in educating the nation's children, UMN provides scholarships in the form of a 50% reduction in fees for teachers/principals and a 30% reduction in fees for children of the employees/staff in high schools/vocational schools (both public and private) who want to continue their education at UMN.
Entry Requirement
- High school graduate majoring in Science, Social Sciences or Languages
- Vocational school graduates of various majors.
Students are required to attend academic guidance meetings at least 3 times per semester. The schedule of the meetings will be provided by the respective academic supervisors. Students have to bring the academic guidance book for the meeting and they need to make sure that the academic supervisor signs it.
Continuing Education Department (CED) is an educational development program at Universitas Multimedia Nusantara (UMN) which is part of the Kompas Gramedia Group. We have various programs in language courses, human development, Testing Centers for national and international certifications, and training programs. UMN’s CED is designed to meet the needs of high school and college students, as well as the public and professionals.
Students are encouraged to find their own companies / agencies for their internships that align with the focus of the Strategic Communication Study Program. Information about available internships can be obtained from other students, social media, job fairs, advertisements in print or electronic media or even through the UMN Career Development Center (CDC).
To complete the Undergraduate Program (S-1) at Multimedia Nusantara University, students must prepare, present, and defend the thesis in front of the thesis examination board, in accordance with the provisions of the study program. The preparation of the thesis is done individually and the students can choose the supervisor directly provided that the selected supervisor agrees.
To complete the Undergraduate Program (S-1) at Multimedia Nusantara University, students must prepare, present, and defend the thesis in front of the thesis examination board, in accordance with the provisions of the study program. The preparation of the thesis is done individually and the students can choose the supervisor directly provided that the selected supervisor agrees.
| Semester | Type | COURSE PLAN | |
| CODE | COURSE | ||
| 1 | Compulsory | UM 122 | English 1 |
| 1 | Compulsory | UM 162 | Pancasila |
| 1 | Compulsory | UM 163 | Civic |
| 1 | Compulsory | JR 112 | Introduction to Journalism |
| 1 | Compulsory | UM 152 | Religiosity |
| 1 | Compulsory | FK 302 | Interpersonal Communication Skill |
| 1 | Compulsory | FK 205 | Bahasa Indonesia for Communication |
| 1 | Compulsory | FK 100 | Introduction to Communication Science |
| 2 | Compulsory | JR 101 | Media Writing |
| 2 | Compulsory | JR 317 | Interview and Reportage |
| 2 | Compulsory | FK 215 | Digital Videography |
| 2 | Compulsory | JR 215 | Photo Journalism |
| 2 | Compulsory | FK 110 | Critical and Creative Thinking |
| 2 | Compulsory | JR 251 | Media Ethics and Law |
| 2 | Compulsory | JR 102 | Narrative Storytelling |
| 3 | Compulsory | JR 108 | Data-driven Storytelling |
| 3 | Compulsory | JR 105 | Audio storytelling |
| 3 | Compulsory | JR 104 | Video Program Production |
| 3 | Compulsory | JR 103 | Indepth and Investigative Reporting |
| 3 | Compulsory | JR 109 | Mobile and Social Media Content Production |
| 3 | Compulsory | JR 107 | Interactive Media Storytelling |
| 3 | Compulsory | JR 106 | Digital Content Production |
| 4 | Compulsory | JR 553 | Media Research Quantitative Methods |
| 4 | Compulsory | JR 654 | Media Research Qualitative Methods |
| 4 | Compulsory | FK 201 | Communication Theory |
| 4 | Compulsory | FK 513 | Academic Writing |
| 4 | Compulsory | JR 652 | Media Studies |
| 4 | Compulsory | JR 637 | Digital Media Management |
| 4 | Compulsory | JR 113 | Media and Intercultural Issues |
| 5 | Compulsory | JR 214 | History of Journalism |
| 5 | Compulsory | JR 411 | English for Journalism |
| 5 | Compulsory | JR 111 | Global Media |
| 5 | Compulsory | JR 349 | Media and Politics |
| 5 | Compulsory | JR 119 | Reporting Bussiness |
| 5 | Compulsory | JR 117 | Media and Environment |
| 5 | Compulsory | JR 538 | Documentary Journalism |
| INTERNSHIP | |||
| 6 | Compulsory | JR 671 | Professional Business Ethics |
| 6 | Compulsory | JR 672 | Industry Experience |
| 6 | Compulsory | JR 673 | Industry Model Validation |
| 6 | Compulsory | JR 674 | Evaluation and Reporting |
| 7 | Compulsory | JR 755/JR 756 | Research proposal Seminar in Journalism or Seminar on Final Project Proposal |
| 7 | Elective | Elective Course | |
| 7 | Elective | Elective Course | |
| 7 | Elective | Elective Course | |
| 7 | Elective | Elective Course | |
| 7 | Elective | Elective Course | |
| 8 | Compulsory | JR 857/JR 858 | Undergraduate Thesis (Study-based) or Undergraduate Thesis (Project-based) |
| Option for Elective Courses: | |||
| 7 | Elective | JR 115 | Media and Humanitarian perspective |
| 7 | Elective | JR 118 | Reporting Sports |
| 7 | Elective | JR 116 | Media and Social Diversity |
| 7 | Elective | JR 6410 | Reporting on Science and Techlonogy |
| 7 | Elective | JR 114 | Entertainment Content production |
| 7 | Elective | JR 332 | News Graphic and Design |
| 7 | Elective | JR 661 | Digital Fact-Checking |
| 7 | Elective | JR 121 | Reporting on Health |
| 7 | Elective | JR 662 | Digital Media Business |
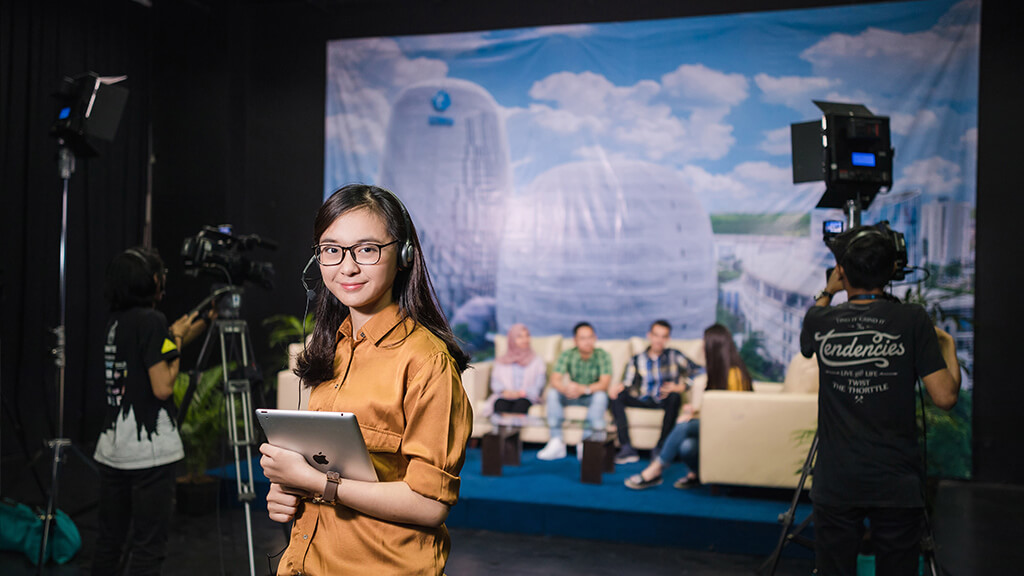
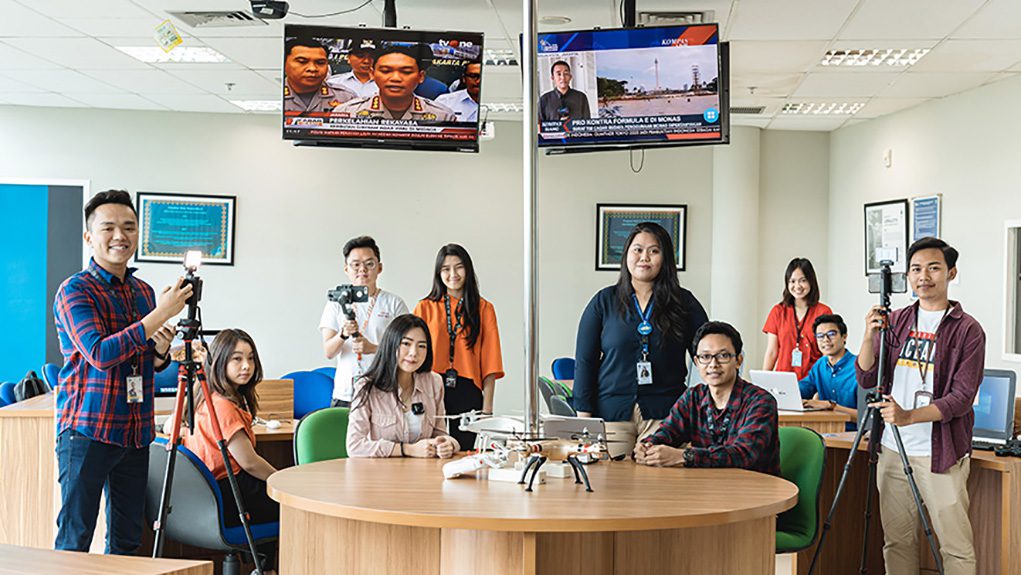
The Journalism Study Program aims to produce graduates who are able to work as multiplatform journalists, multimedia content producers, and researchers in the field of convergence journalism. The study program offers a curriculum for journalism students with strong journalistic competencies based on national guidelines on higher education and the association of communication science higher education or ASPIKOM as well as international journalism curriculum standards.
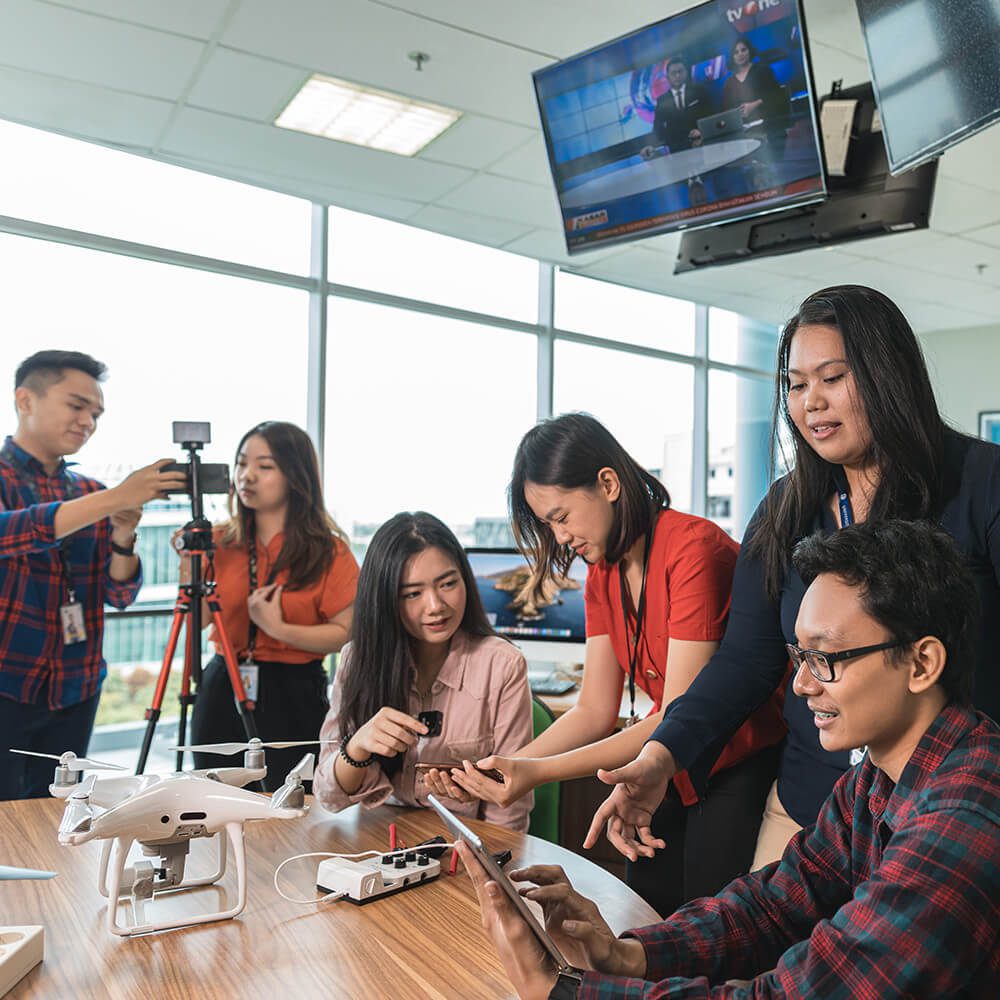
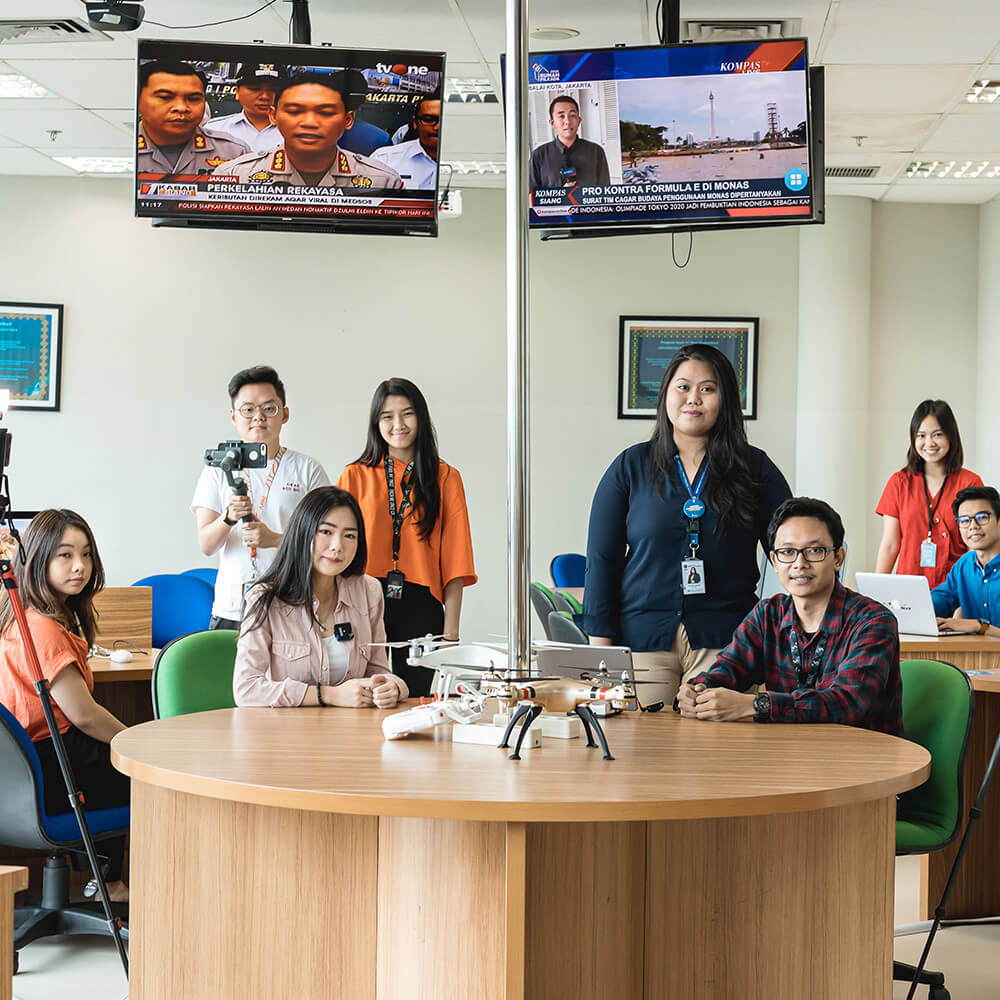
Through hands-on experiential learning methods equipped with modern library facilities, and digital collaborative laboratory infrastructures, students are invited to explore new forms of journalism, such as virtual reality journalism, augmented reality journalism, data journalism, drone journalism, visual journalism, mobile journalism, and others. Furthermore, the curriculum study program aims to:
- Produce professional multiplatform journalists and learners who are able to apply fact-based multimedia journalism knowledge that is independent, ethical, creative, analytical, and has skills in evaluating, developing, reviewing, and producing journalistic and other fact-based works.
- Produce professional media practitioners and learners who have independent, ethical, critical, creative, and entrepreneurial multimedia journalism knowledge to develop, review, and produce factual-based journalism works.
Produce professional individuals and learners who have an independent, ethical, creative, critical, and analytical attitude in evaluating, developing, reviewing, and producing journalistic and other fact-based works
|
ELO CODE |
KEYWORDS |
ELO DESCRIPTION |
| ELO 1 | lifelong learner, self-reliant, religious, ethical | Able to become a lifelong learner who has a spirit of independence in accordance with religiosity and ethical values. |
| ELO 2 | humanity, environment, law | Able to contribute to society that upholds human values, the environment, and the rule of law. |
| ELO 3 | responsibility | Able to be responsible for the journalistic work produced in accordance with the rules and useful for the community. |
| ELO 4 | theories & concepts, communication, journalism, relevant sciences | Able to demonstrate knowledge, theories and concepts in the fields of communication, basic journalism, and relevant sciences well. |
| ELO 5 | knowledge, implementation of communication theory, journalism, national/global issues | Able to demonstrate knowledge of the implementation of communication and journalism theories to address issues at the national and international levels. |
| ELO 6 | logical, critical, innovative, analytical thinking, fact-based work | Able to think logically, critically, and innovatively based on data analysis in producing journalistic works or other fact- based works for the media. |
| ELO 7 | media management, collaboration, fact- based work | Able to apply the knowledge in the field of media management and able to collaborate in groups in producing journalistic works and other fact-based works for the media. |
| ELO 8 | Entrepreneurship principle and application, production management, ICT-based | Able to apply the principles of entrepreneurship and production management of journalistic works and other fact-based works that utilize ICT technology. |
| ELO 9 | scientific research, analysis, media- journalism industry | Able to conduct research in the field of journalism according to scientific principles by prioritizing the usefulness of research for the development of the media industry, community empowerment, and analysis of links between various fields of science and journalism. |
| ELO 10 | journalistic/factual- based production, innovative, ICT- based | Able to produce journalistic works or innovative fact-based works by utilizing ICT technology. |
Graduates of this study program are expected to become multi-platform journalists, producers of multimedia content, and researchers in the field of media and journalism. The journalism graduates will be:
- Individuals who have knowledge in the field of fact-based multimedia journalism utilizing digital technology.
- Individuals who have an independent, ethical, critical, analytical, creative, and entrepreneurial attitude to develop factual-based works.
- Individual learners who have the skills to evaluate, develop, review, and produce journalistic and other fact-based works.
| Location of the study program or HEI site(s)/location where the program is provided | Tangerang, Indonesia |
| Faculty/Department | Faculty of Communication |
| Academic Degree | Bachelor of Journalism |
| Date or planned date of introduction |
13.09.2016 (Decree Number 387/KPT/I/2016) 2016/2017 Academic Year (First Cohort) |
|
Status last national accreditation (incl. result) Status last int. accreditation (incl. result) |
Accredited by BAN-PT No. 4451/SK/BAN-PT/Ak.Ppj/S/X/2023. According to BAN-PT the study program has met the quality of higher education standards (B). |
| Subject field | Journalism |
| Regular study duration | 8 semesters or 4 years |
| Number of (ECTS) credits | 144 SKS (241,92 ECTS) |
| Enrollment period(s) | Odd semester |
| Frequency of the offered program | 1 in year |
| Capacity per year | 120 |
| Number of students currently enrolled | 519 |
| Average number of graduates per year | 117 (2017-2021) |
| Target group(s) | Students with social science and general background |
| Admission requirements |
|
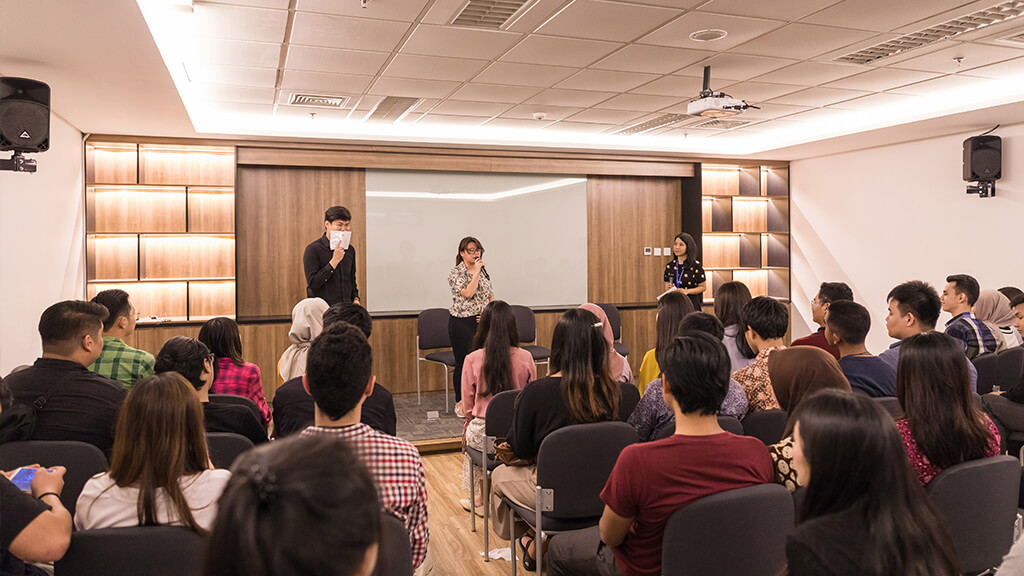
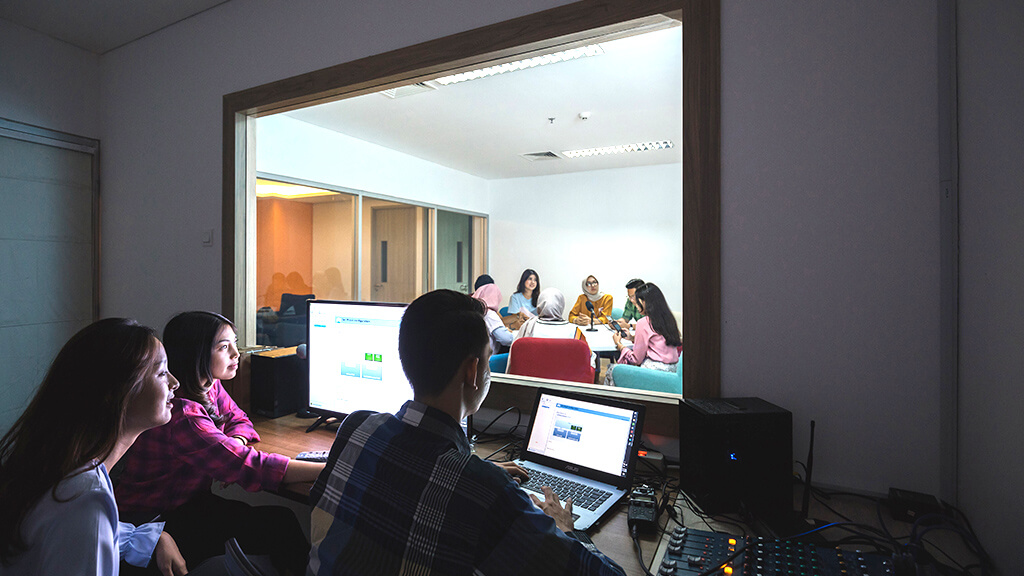
To support the learning process, umn provided a complete and sophisticated college facility, according to industrial standards. Through the existence of the facility, students have been invited to be close to the industrial world since sitting in college and to have competence that matches the needs of the industry. That way, it will make it easier for umn students to find jobs, even before graduation.
Extracurricular Student Activities
In order to help students explore and develop their non-academic potentials, UMN also provides a variety of extra-curricular activities for students which is locally called UKM, Student Activity Unit.

SEE OTHER
UMN’S STUDENT ACTIVITIES
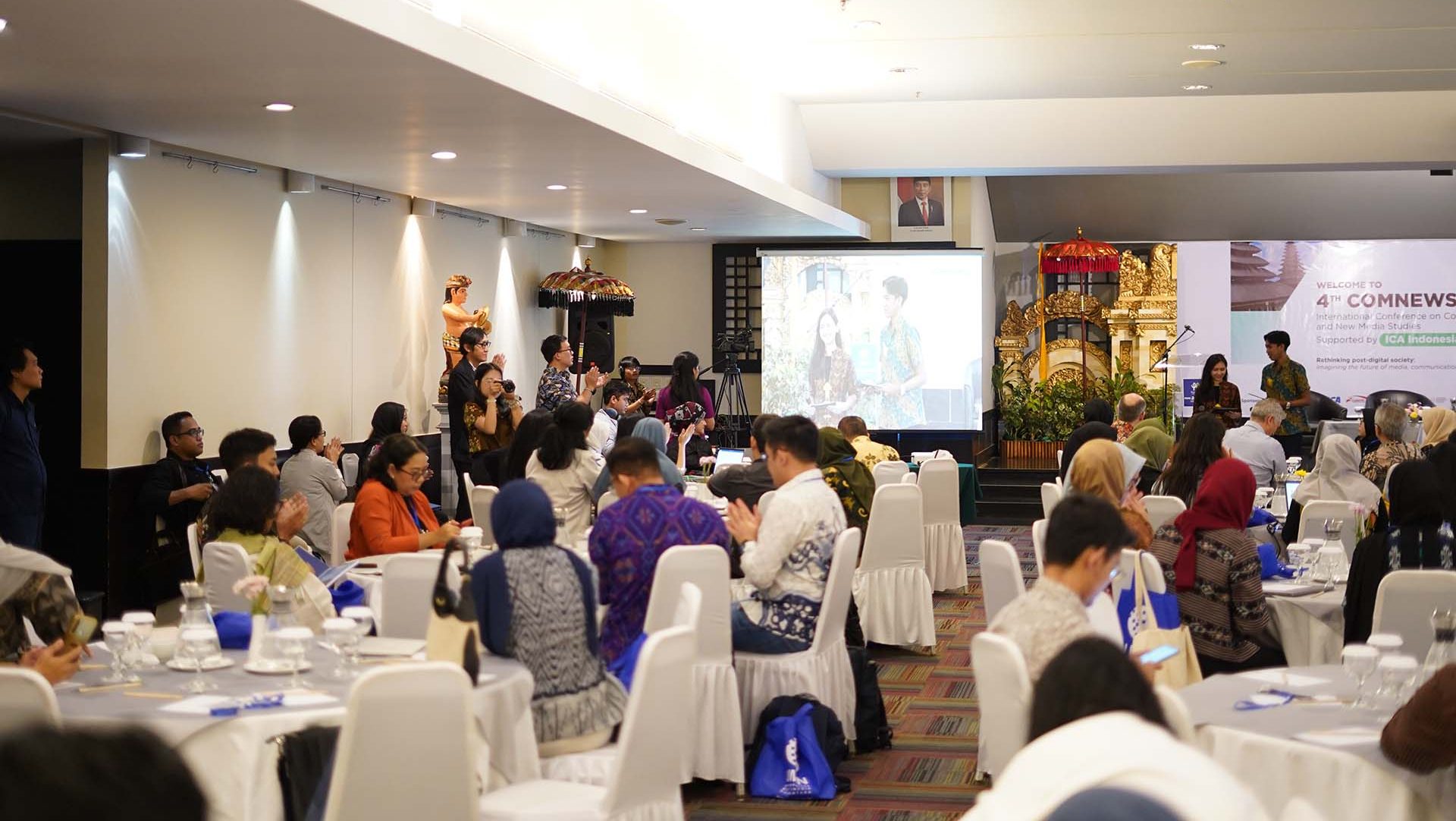
Conference on Communication and New Media Studies (COMNEWS 2025)
COMNEWS 2025 showcases innovative ideas and interdisciplinary collaboration to address today’s communication challenges, highlighting how AI, IoT, and advanced systems support sustainability through energy efficiency and green infrastructure.
Recapitulation of Internal Research – Journalism
Recapitulation of DIKTI Grant Research – Journalism
List of Lecturer Community Outreach Activities
Recapitulation of Copyright Innovation – Journalism
TESTIMONIAL

“From UMN, I got a lot of useful knowledge in the world of work. Lecturers who are also practitioners always provide insight into the media industry so that students don't stutter when working. The curriculum provided is also in accordance with industry needs so that UMN graduates are ready to work in television stations, radio, print media, and online media.”
Jessica Damiana
Journalism 2014 | Junior Executive at Telum Media

"Journalism studies at UMN not only emphasize academic excellence, but also train students to collaborate effectively with others. In addition, character education is strongly emphasized to shape individuals who are wise, principled, and impactful."
Diana Valencia
Journalism 2015 | News Anchor at CNN Indonesia TV
CERTIFICATION
Information Literacy
Information literacy is an ability that individuals have in determining, searching, managing and evaluating information effectively and efficiently. This training is open to UMN active students. For further information, please contact: library.umn.ac.id
Adobe Certification
Adobe is a fundamental software suite widely used in the film and animation industry. Recognizing this need, UMN provides Adobe certification programs, available either individually or as a complete package. For more information, please contact the Center for Enrichment and Development (CED).
“During my time in UMN’s Journalism Program, all the courses taught provided a great base for the future in media industry. In addition, I also feel that UMN educates its students to be able to adapt and communicate in various walks of life, which is certainly very useful for me to apply in my current world of work.”
David Caessarre
Alumni Jurnalistik 2015
Creative Officer di Narasi TV
Journalism
“Multimedia Nusantara University’s Journalism Study Program focuses on utilizing new technologies to learn new forms of journalism. Therefore, learning activities are also supported with adequate technology. Some courses are also tailored to the needs of the industry as well as the development of existing technologies, such as mobile and social media journalism courses that utilize the use of gadgets in producing and disseminating journalistic products through social media.”





























 Commnews 2023.jpg)






